
Localization marketing adapts brand messaging, visuals, and strategies to fit cultural, linguistic, and behavioral norms of target markets. Beyond translation, it ensures authentic engagement, optimizes platform use, respects local customs, and continuously tests campaigns for global success.
Global expansion sounds thrilling until you realize your carefully crafted marketing message just doesn’t translate. Literally. What resonates with customers in New York might fall completely flat in Tokyo, and that clever tagline that works in English could become confusing—or worse, offensive—in another language.
Localization marketing goes far beyond simple translation. It’s about adapting your entire marketing strategy to connect authentically with local audiences, considering their cultural nuances, buying behaviors, and communication preferences. Companies that master localization see significantly higher engagement rates and revenue growth in international markets.
Understanding the Difference Between Translation and Localization
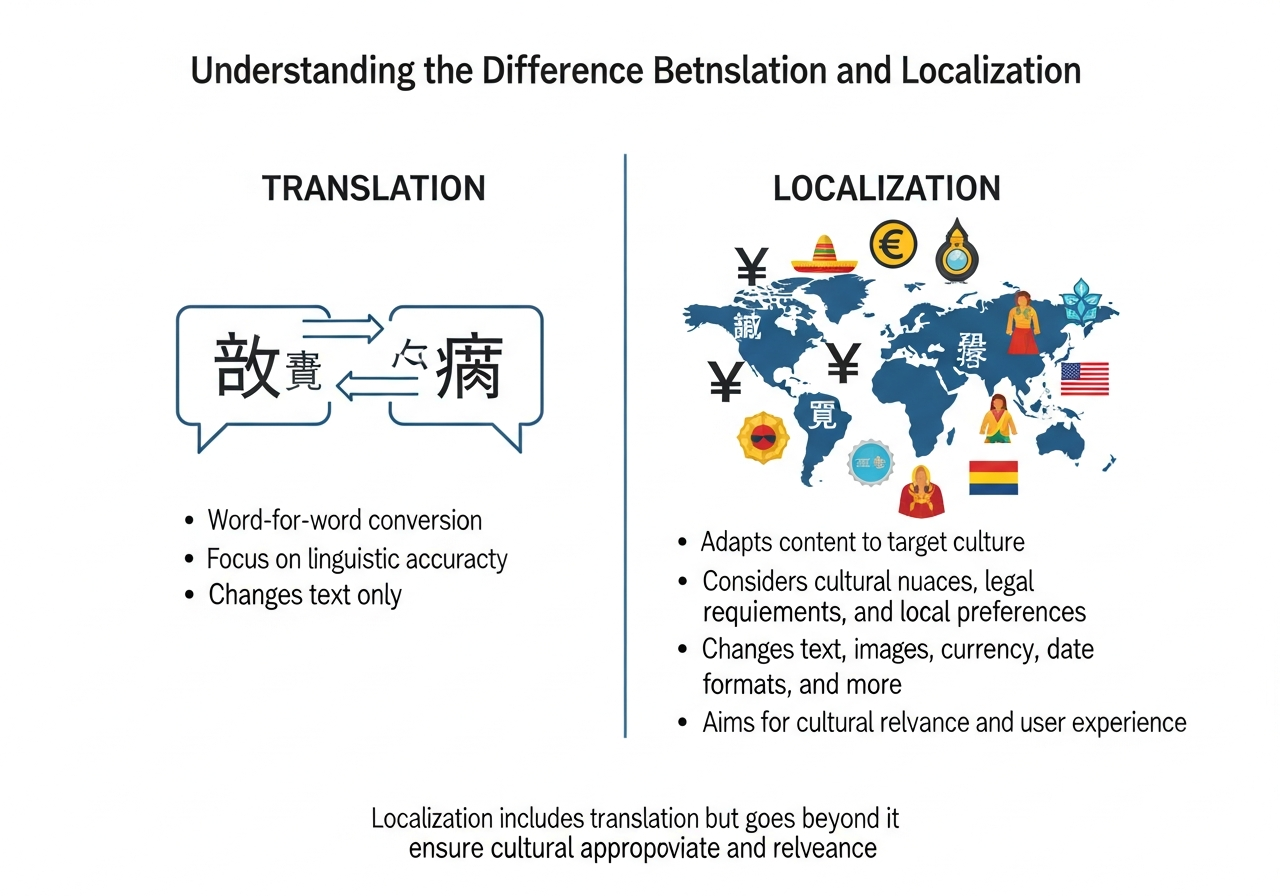
Translation converts text from one language to another. Localization transforms your entire marketing approach to fit local markets. The distinction matters more than you might think.
Translation focuses on linguistic accuracy—ensuring words and phrases convey the same meaning across languages. Localization considers context, culture, and local market dynamics. It adapts imagery, colors, messaging tone, product positioning, and even business models to align with local expectations.
Consider McDonald’s approach. The company doesn’t just translate “Big Mac” into local languages. In India, they offer vegetarian options and avoid beef entirely. In Japan, they serve rice burgers. These adaptations reflect deep localization that respects local dietary preferences and cultural values.
Effective localization marketing requires understanding what drives purchasing decisions in each market. Price sensitivity, brand loyalty patterns, preferred communication styles, and shopping behaviors all vary significantly across cultures.
Research Your Target Markets Thoroughly
Successful localization starts with comprehensive market research. Generic assumptions about international audiences lead to costly marketing mistakes and missed opportunities.
Demographic and psychographic analysis forms your foundation. Age distribution, income levels, education, and lifestyle preferences shape how people respond to marketing messages. A luxury brand targeting millennials in Germany will need different messaging than the same brand targeting baby boomers in Brazil.
Cultural values and communication styles directly impact campaign effectiveness. Some cultures prefer direct, straightforward messaging, while others respond better to subtle, relationship-focused approaches. High-context cultures rely heavily on implied meaning and visual cues, while low-context cultures prefer explicit, detailed information.
Competitive landscape research reveals market saturation levels and successful positioning strategies. Understanding local competitors helps you identify differentiation opportunities and avoid oversaturated messaging approaches.
Regulatory and legal considerations prevent costly compliance issues. Advertising standards, data privacy laws, and industry-specific regulations vary dramatically between markets. What’s perfectly acceptable marketing in one country might violate regulations in another.
Use surveys, focus groups, and local partnerships to gather insights. Social media listening tools help you understand conversation patterns and sentiment around your industry or competitors in different markets.
Adapt Your Messaging and Tone
Global marketing presents a unique challenge: how to communicate consistently while respecting the diverse cultural, social, and linguistic nuances of different markets. Your brand voice must be flexible enough to resonate locally, yet consistent enough to maintain a recognizable identity worldwide.
1. Maintain Core Brand Identity
While local adaptations are essential, your brand’s core identity—its mission, values, and overarching personality—must remain constant. This ensures that no matter the market, customers recognize your brand and understand its promise.
Actionable Tip: Create a “global brand framework” that defines your brand voice, tone, and key messaging pillars. Use this framework as the foundation for all market-specific adaptations.
2. Adjust Tone for Cultural Preferences
Even subtle changes in tone can have a significant impact. Marketing styles vary across cultures:
-
Direct and assertive: In markets like the U.S., Germany, or Australia, bold claims and clear CTAs like “Buy Now” or “Sign Up Today” are effective.
-
Humble and relationship-focused: In markets like Japan, Korea, or Scandinavia, messaging that emphasizes community, harmony, and subtle persuasion is more effective.
Example: A tech company promoting productivity software could highlight rapid results in the U.S., whereas in Japan, it might emphasize reliability, team collaboration, and long-term efficiency.
3. Carefully Use Humor and Cultural References
Humor and pop culture references rarely translate directly across cultures. A joke that resonates in one country may confuse or even offend audiences in another.
Strategies:
-
Use universally understandable humor or emotional storytelling.
-
Localize campaigns with region-specific creative teams who understand cultural context.
-
When in doubt, avoid humor that relies on idioms, slang, or local events.
Example: A marketing campaign using a pun in English might fail in Japanese or French markets; instead, create a localized version that evokes similar emotions without relying on wordplay.
4. Reposition Value Propositions for Local Priorities
Customer priorities differ across regions. Products or services may need to be reframed to match local values, lifestyles, or economic conditions.
Examples:
-
Productivity apps: Emphasize speed and efficiency in fast-paced urban markets; highlight work-life balance in regions prioritizing leisure.
-
Eco-friendly products: Focus on sustainability benefits in environmentally conscious markets; emphasize cost savings or health benefits where environmental concerns are secondary.
5. Adapt Call-to-Action (CTA) Language
CTAs are culturally sensitive. A directive phrase like “Buy Now” may motivate immediate action in direct cultures but can feel aggressive in more relationship-focused societies.
Strategies:
-
Test softer CTAs, such as “Discover how this can help you” or “Learn more,” in markets that favor subtlety.
-
Combine urgency with value in direct cultures: “Order today to save 20%!”
6. Language and Localization
Translation alone is insufficient. True localization involves adapting idioms, measurements, currency, visuals, and even color symbolism.
Example: Red may convey luck in China but signal danger in some Western cultures. Similarly, images and gestures should reflect local social norms to avoid miscommunication.
7. Document and Train Teams
Consistency across multiple markets requires detailed documentation and training. Create market-specific brand voice guidelines that include:
-
Tone adjustments per culture
-
CTA language preferences
-
Examples of localized campaigns
-
Dos and don’ts for humor and visuals
Train marketing teams, regional partners, and agencies to follow these guidelines while still leaving room for creativity.
8. Test, Iterate, and Optimize
No adaptation strategy is perfect from the start. Conduct market-specific A/B testing, surveys, and focus groups to assess how your messaging resonates. Use insights to refine language, tone, visuals, and CTAs for each region.
Key Metrics to Monitor:
-
Engagement rates (click-throughs, time on page)
-
Conversion rates by market
-
Social media sentiment and shares
-
Customer feedback on tone and messaging clarity
Visual Elements and Design Considerations
Visual communication transcends language barriers, but cultural interpretations of imagery, colors, and design vary significantly. Your visual strategy needs localization just as much as your copy.
Color psychology differs dramatically across cultures. White symbolizes purity in Western cultures but represents mourning in some Asian cultures. Red signifies luck and prosperity in China but can indicate danger or warning in other contexts. Research color associations thoroughly before finalizing visual campaigns.
Image selection should reflect local demographics and cultural values. Stock photos featuring people should represent your target audience authentically. Avoid imagery that might be culturally inappropriate or exclude significant population segments.
Layout and design preferences vary by market. Some cultures read right-to-left, affecting how people scan visual content. Dense, information-heavy layouts work well in some markets but overwhelm audiences in others. Clean, minimalist designs appeal to certain cultures while appearing sparse or low-value to others.
Religious and cultural sensitivities around imagery require careful attention. Clothing styles, gestures, religious symbols, and even architectural elements can carry unintended meanings. Work with local teams or consultants to review visual content before launch.
Create region-specific asset libraries that maintain brand consistency while respecting local visual preferences and cultural norms.
Platform Selection and Local Channels
Social media and digital marketing platforms vary in popularity and usage patterns across different markets. Your channel strategy needs localization to reach audiences where they actually spend time.
Platform popularity differs significantly by region. Facebook dominates in many markets but has limited presence in others. WeChat serves as a primary communication and commerce platform in China, while WhatsApp fills similar roles in Latin America. Research active user bases and engagement patterns for each platform in your target markets.
Content consumption preferences vary by platform and culture. Video content might perform exceptionally well on certain platforms in specific markets while falling flat in others. Some audiences prefer long-form written content, while others engage primarily with visual or audio content.
E-commerce integration capabilities differ across platforms and regions. Some markets rely heavily on social commerce features, while others prefer separate e-commerce experiences. Align your platform strategy with local purchasing behaviors and technological adoption patterns.
Local influencer ecosystems provide authentic connection opportunities. Partner with influencers who genuinely resonate with local audiences rather than simply translating content from influencers in other markets. Local influencers understand cultural nuances and communication styles that international figures might miss.
Develop platform-specific content calendars that align with local events, holidays, and cultural moments while maintaining overall brand consistency.
Test and Optimize Continuously
Localization marketing requires ongoing refinement based on real performance data and audience feedback. What works initially might need adjustment as markets evolve and you gain deeper cultural insights.
A/B testing becomes more complex but more valuable when localizing campaigns. Test different messaging approaches, visual styles, and calls-to-action within each market. Don’t assume that winning elements from one market will perform well in others.
Performance metrics might require reinterpretation based on local behaviors. Click-through rates, engagement patterns, and conversion timelines vary across cultures. Establish market-specific benchmarks rather than applying universal standards.
Feedback collection methods should align with local communication preferences. Some cultures readily provide direct feedback through surveys, while others prefer indirect feedback channels or require relationship-building before sharing honest opinions.
Local partnerships provide ongoing market insights and cultural guidance. Work with local agencies, consultants, or team members who can provide real-time feedback on campaign performance and cultural relevance.
Seasonal and cultural calendar integration helps you capitalize on local opportunities and avoid cultural missteps. Religious holidays, national celebrations, and cultural observances create natural engagement opportunities or periods when marketing should be paused entirely.
Building Your Global Localization Strategy

Successful localization marketing transforms international expansion from a translation exercise into authentic relationship building. The brands that succeed globally don’t just speak local languages—they understand local values, preferences, and communication styles.
Start with thorough market research and cultural understanding before developing any creative materials. Invest in local partnerships and team members who can provide ongoing insights and feedback. Remember that localization is an ongoing process, not a one-time project.
Ready to expand your marketing reach globally? Begin by selecting one target market and implementing these localization strategies systematically. Measure results, gather feedback, and refine your approach before scaling to additional markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between translation and localization?
Translation converts text to another language, while localization adapts messaging, visuals, and strategy to align with cultural norms, local behaviors, and market expectations.
2. Why is market research important for localization?
Thorough research identifies cultural values, buying behaviors, platform preferences, legal considerations, and local competition, ensuring campaigns resonate and avoid costly mistakes.
3. How should messaging and tone be adapted?
Adjust brand voice, tone, humor, and value propositions to reflect local cultural preferences while maintaining overall brand identity. Test calls-to-action for effectiveness in each market.
4. What visual elements require localization?
Colors, imagery, layout, and design should align with local cultural interpretations, religious sensitivities, and reading habits to ensure relevance and avoid offense.
5. How do platform choices impact localization?
Social media, digital platforms, and e-commerce usage vary by region. Selecting local platforms and influencers maximizes reach, engagement, and cultural authenticity.
6. Why is continuous testing and optimization necessary?
Local audience behaviors, seasonal trends, and cultural norms evolve. A/B testing, performance analysis, and feedback loops ensure campaigns remain effective and culturally relevant.
7. How can brands start their global localization strategy?
Begin with one target market, implement research-based localization strategies, gather feedback, measure results, and refine before expanding to additional markets.
Leave a Reply